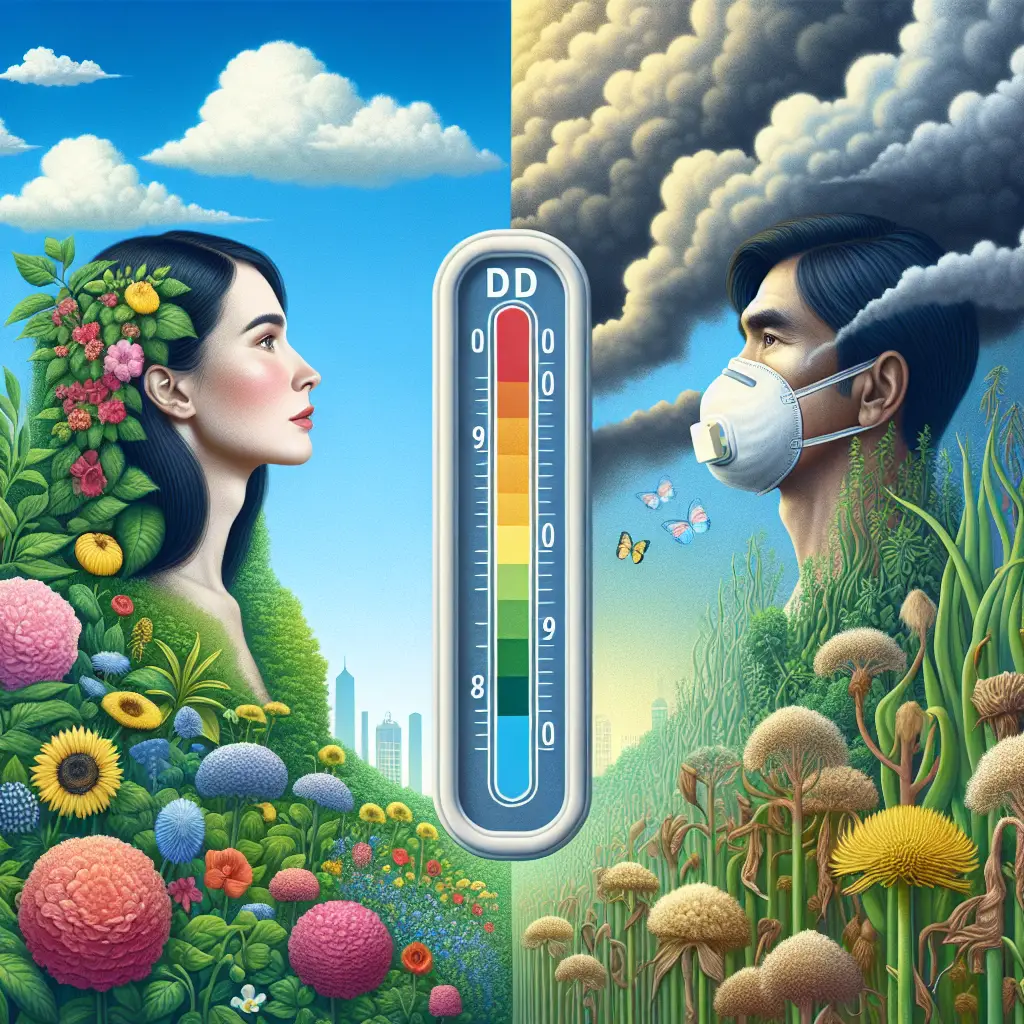
Air Quality Index and Impact on Human and Plant Health
The Air Quality Index (AQI) is a critical measure that helps us understand the quality of air in our environments and its potential effects on both human and plant health. As the world becomes increasingly urbanized and industrialized, monitoring air quality becomes vital for promoting public health and environmental sustainability.
What is the Air Quality Index?
The AQI is a numerical scale that represents the concentration of major air pollutants over a specified time. This includes:
- Particulate Matter (PM2.5 and PM10)
- Nitrogen Dioxide (NO2)
- Ozone (O3)
- Sulfur Dioxide (SO2)
- Carbon Monoxide (CO)
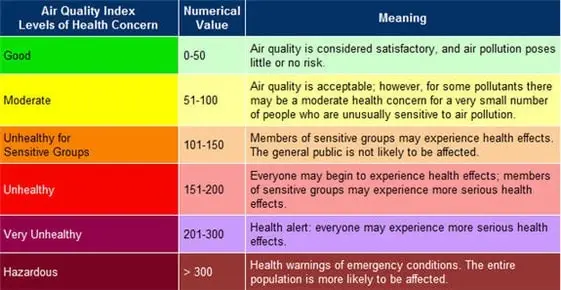
These pollutants are measured in parts per million (ppm) or micrograms per cubic meter (µg/m3). The AQI scale typically ranges from 0 to 500, with higher values indicating worse air quality. Different countries have their own standards for AQI, but the interpretation remains generally similar:
- 0-50: Good
- 51-100: Moderate
- 101-150: Unhealthy for sensitive groups
- 151-200: Unhealthy
- 201-300: Very Unhealthy
- 301-500: Hazardous
Impact of Air Quality on Human Health
Short-term Effects
Poor air quality can cause immediate health issues, particularly for vulnerable groups such as children, the elderly, and individuals with pre-existing health conditions. Short-term exposure to elevated AQI levels can lead to:
- Respiratory Irritation: Inflamed airways and exacerbated asthma or bronchitis.
- Eye Discomfort: Itchy and watery eyes.
- Physical Fatigue: General tiredness and decreased energy levels.
Long-term Effects
Chronic exposure to air pollution poses significant health risks, including:
- Cardiovascular Diseases: Increased risk of heart attacks and strokes.
- Lung Diseases: Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and lung cancer.
- Developmental Issues in Children: Potential impairment in lung growth and cognitive development.
Maintaining awareness of the AQI in your area is crucial for minimizing these risks. This is why health advisories often recommend limiting outdoor activities during high pollution days.
Impact of Air Quality on Plant Health
Photosynthesis and Growth
Plants are highly sensitive to air quality, and pollutants can severely disrupt the process of photosynthesis. Contaminants like ozone cause:
- Stomatal Closure: Hindering the exchange of gases.
- Chlorosis: Yellowing of leaves as chlorophyll breaks down.
Prolonged exposure to pollutants can reduce plant growth rates and agricultural productivity, impacting food supply chains and ecosystems.
Soil and Water Quality
Air pollution doesn’t just affect plants directly. Pollutants can settle on soil and water, leading to:
- Soil Acidification: Changing the pH and affecting nutrient absorption.
- Water Contamination: Harmful to both aquatic plants and land-based plants using water sources for irrigation.
Ecological Imbalances
Polluted environments can favor the growth of certain species (like pollutants-resistant weeds), disrupting biodiversity and altering habitats, further compounding ecological imbalances.
Steps to Improve Air Quality
Efforts from individuals, communities, and governments are crucial to improving air quality:
- Emission Controls: Implementing stricter regulations on industrial emissions and vehicular emissions.
- Adopting Clean Energy: Transitioning to renewable energy sources like solar, wind, and hydropower.
- Enhancing Green Spaces: Planting more trees and maintaining urban greenery to absorb pollutants.
- Public Awareness: Informing citizens about the effects of air pollution and promoting sustainable practices.
Conclusion
Understanding the Air Quality Index provides valuable insights into the environment we live in and its impact on health. Human and plant health are inextricably linked to the quality of the air we breathe, making it imperative to adopt measures that enhance air quality. By taking proactive steps, we can mitigate the adverse effects of air pollution, ensuring a healthier and more sustainable world for future generations.










